A STUDY ON GROWTH PERFORMANCE OF CROP INSURANCE SCHEMES IN ANDHRA PRADESH AND INDIA.
0 Views
M. MARY SHARON*, B. APARNA, S.RAJESWARI and B. RAVINDRA REDDY
Department of Agricultural Economics, S.V.Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517 502, Chittoor Dt., A.P., India
ABSTRACT
Agriculture is an important sector of the Indian economy, accounting for 15.87 per cent of the nation’s GDP, about half of the population still relies on agriculture. It is varied, diversified and prone to a variety of risks. It is highly risky venture due to both uncertainty in crop production and volatility in prices. The compound growth rates in performance of NAIS in India were calculated for number of farmers insured, area insured, sum insured, gross premium, farmers’ premium and number of farmers benefitted, growth rates were calculated as 10.43, 8.98, 21.49, 23.1, 23.25 and 13.93 respectively. Same as for WBCIS in India were calculated, the number of farmers insured, area insured, sum insured, gross premium, farmers’ premium and claims, growth rates were calculated as 50.48, 44.19, 41.82, 47.85, 58.67 and 57.32 respectively. The growth performance of National Agricultural Insurance Scheme in Andhra Pradesh the growth rates were found to be positive for the aspects like number of farmers insured with 0.09, sum insured with 10.40, gross premium 16.98 and premium subsidy with 0.25. For some terms like area insured, claims paid with and number of farmers benefitted, compound growth rates were found to be negative with the values of -0.27, -17.85 and -29.64 respectively. For Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme in Andhra Pradesh the compound growth rates were found to be positive for all the aspects but maximum growth rate was observed for area insured with 232.83 for number of farmers insured, sum insured, gross premium, premium subsidy, claims paid and number of farmers benefitted, growth rates were calculated as 167.03, 142.36, 153.29, 182.65, 146.96 and 159.8 respectively.
KEYWORDS:
WBCIS, NAIS, PMFBY, growth performance, crop insurance
INTRODUCTION
The agriculture sector plays a pivotal role in growth of economy and in lives of people. Despite technological and economic advancements, the condition of farmers continues to be unstable due to natural calamities and price fluctuations. In some extreme cases, these unfavorable events become one of the factors leading to farmer’s suisides which are now assuming serious proportions (Raju and Chand, 2007). Crop insurance helps in stabilization of farm production and income of the farming community. It helps in optimal allocation of resources in the production process. Crop insurance not only stabilizes the farm in-come but also helps the farmers to initiate production ac-tivity after a bad agricultural year.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Secondary data were collected from Agriculture Insurance Company (AIC) of India. The statistical data about number of farmers covered under NAIS, WBCIS and PMFBY, total area covered, total premium collected, total subsidy amount received and total claims amount were collected.
Growth rate analysis:
Compound growth rates were calcualted for num-ber of farmers insured, area covered, sum insure, pre-mium collected, subsidy provided claims paid and number farmers benefited under crop insurance schemes in study area (Rathore et al., 2011).

RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Growth performance of National Agricultural Insurance Scheme in India
The growth performance of National Agricultural Insurance Scheme in India is given in Table 1 in terms of average area, number of insured farmers, premium paid, sum insured, claim amount and number of farmers benefitted from 1999-2000 to 2015-16. The compound growth rates in performance of NAIS in India were calculated and have been reported found progressive. The compound growth rates were found to be positive for all the aspects but maximum growth rate was observed for claims paid to farmers with 26.11 which is loss to the government. For number of farmers insured, area insured, sum insured, gross premium, farmers’ premium and number of farmers benefitted, growth rates were calculated as 10.43, 8.98, 21.49, 23.1, 23.25 and 13.93 respectively (Kumbalep and Devaraju, 2018).
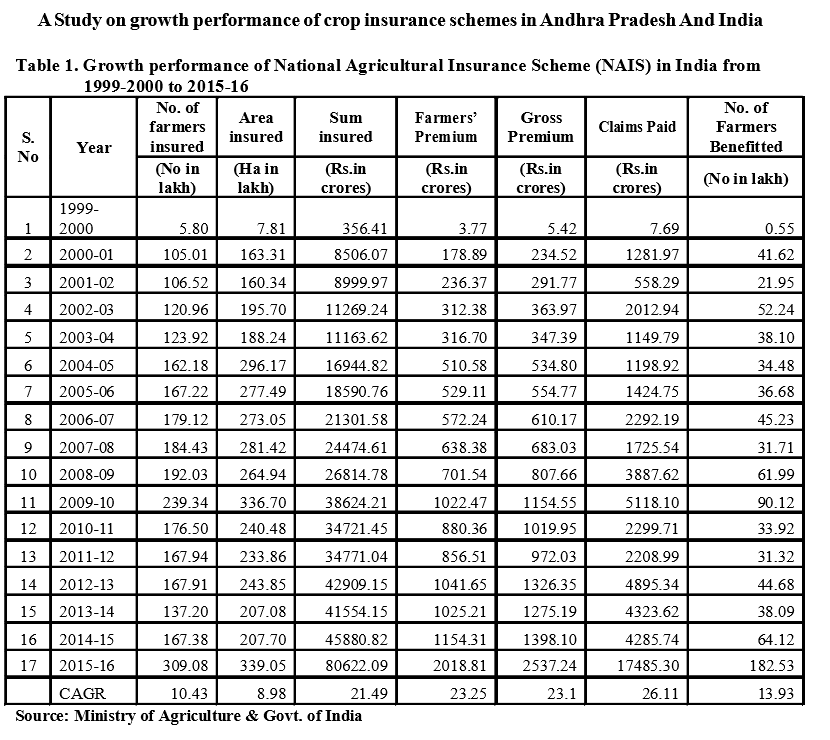
Growth performance of Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme in India
The growth performance of Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme in India is given in Table 2 in terms of area covered, number of insured farmers, premium collected, sum insured and claim amount from 2007-08 to 2015-16. The compound growth rates in performance of WBCIS in India were calculated and have been reported found progressive. The compound growth rates were found to be positive for all the aspects but maximum growth rate was observed for number of farmers benefitted which is good to farmers. For number of farmers insured, area insured, sum insured, gross premium, farmers’ premium and claims, growth rates were calculated as 50.48, 44.19, 41.82, 47.85, 58.67 and 57.32.
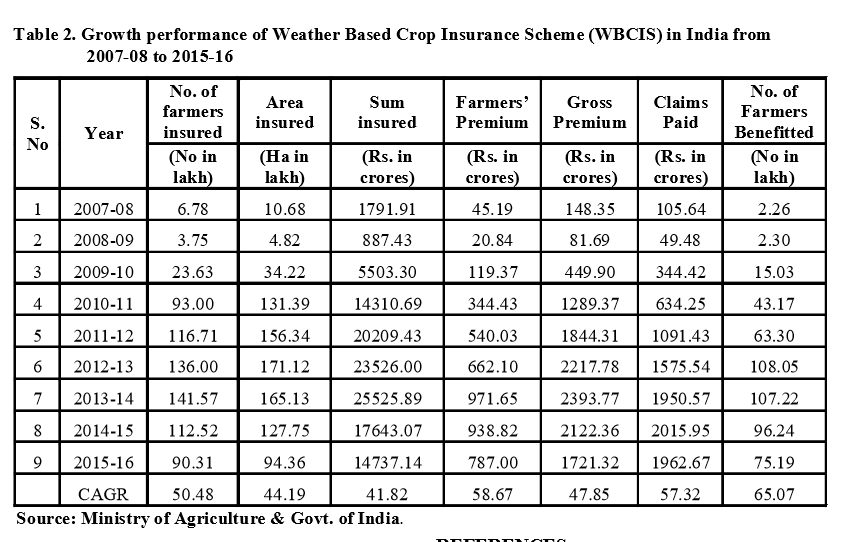
Growth performance of National Agricultural Insurance Scheme in A.P
The growth performance of National Agricultural Insurance Scheme in Andhra Pradesh is given in Table 3 in terms of average area covered, number of insured farmers, premium paid, sum insured and claim amount from 2000-01 to 2013-14. The compound growth rates were found to be positive for the aspects like number of farmers insured with 0.09, sum insured with 10.40, gross premium 16.98 and premium subsidy with 0.25. For some terms like area insured, claims paid with and number of farmers benefitted, compound growth rates were found to be negative with the values of -0.27, -17.85 and -29.64 respectively. But maximum growth rate was observed for gross premium paid by farmers which is loss to the farmers (Dey and Maitra, 2017).
REFERENCES:
Dey, K and Maitra, D. 2017. Agriculture insurance in India. Economic & Political Weekly. 52 (52) :88-96.
Gondala, V. L., Khuni, A. L and Vekariya, S. B. 2008. Impact and progress of crop insurance programme in Gujarat State. Agricultural Situation in India
Kumbalep, S and Devaraju M. 2018. Awareness and perception of farmers about crop insurance – A study in Kolar District of Karnataka State. International Journal of Advances in Science Engineering and Technology. 6(1) : 90-94.
Raju, S.S and Chand, R. 2008. Progress and problems in agricultural insurance in India. Economic and Political Weekly. 24 (21): 1905-1908.
Rathore, V.S., Burark, S.S and Jain, H.K. 2011. Performance of crop insurance scheme in Udaipur District of Rajasthan. Agricultural Economics Research Review. 24: 25-35.
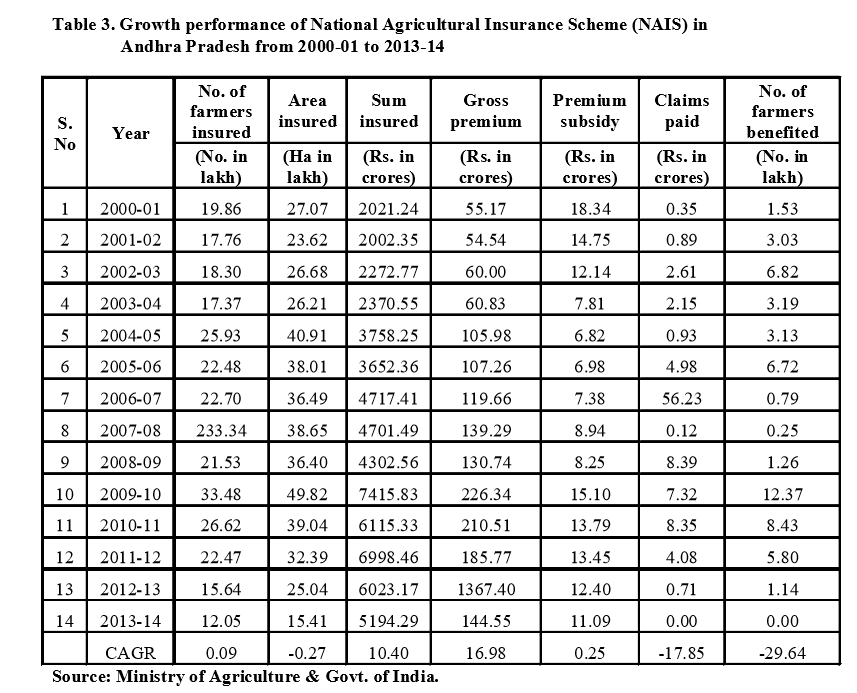
Coverage of Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme in A.P
The coverage of Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme in Andhra Pradesh is presented in Table 4.10 in terms of average area covered, number of insured farmers, premium paid, sum insured and claim amount from 200910 to 2013-14. Maximum number of farmers covered in 2012-13 with 9.32 lakh farmers and 15.17 lakh ha. On the whole, WBCIS has performed well in terms of coverage of farmers and benefits extended to the farmers (Gondala et al., 2008).
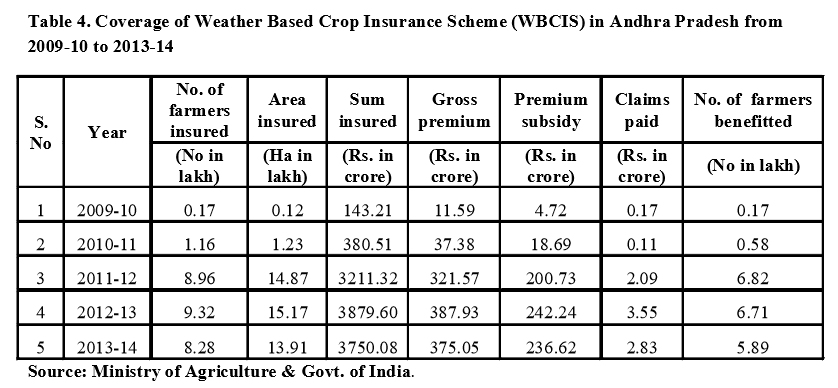
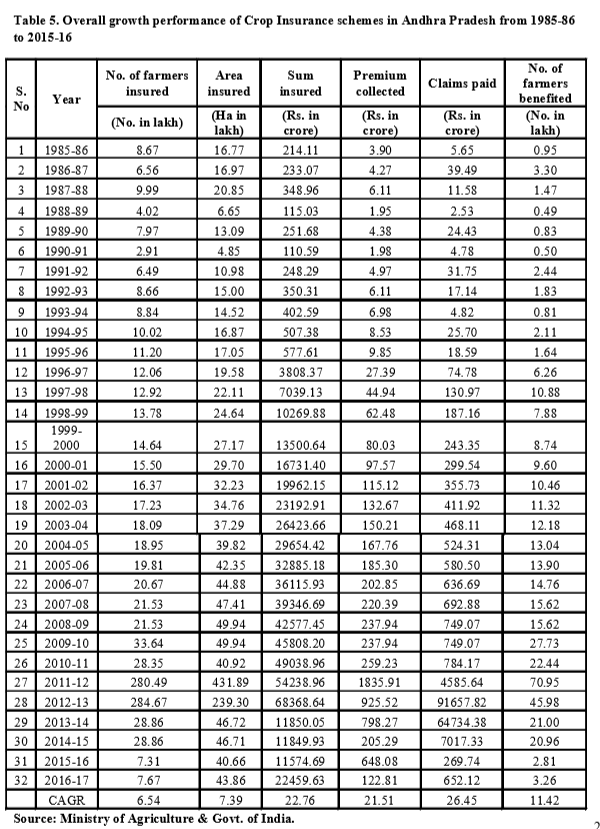
Overall growth performance of crop insurance schemes in A.P
The overall growth performance of Crop Insurance Schemes in Andhra Pradesh is given in Table 5 in terms of average area, number of insured farmers, premium paid, sum insured, claim amount and number of farmers benefitted from 1985-86 to 2015-16. The compound growth rates were calculated and have been reported found progressive. The compound growth rates were found to be positive for all the aspects but maximum growth rate was observed for claims paid to farmers with 26.45 which is loss to the government. For number of farmers insured, area insured, sum insured, premium collected and number of farmers benefitted, growth rates were calculated as 6.54, 7.39, 22.76, 21.1 and 11.42
CONCLUSION:
In India, crop insurance started with CCIS in 1985 and it was in operation up to 1999. Later NAIS came into operation in 1999 and covered 2712.05 lakh farmers. The compound growth rates were found to be positive for average area, number of insured farmers, premium paid, sum insured and claims paid and number of farmers benefitted. In Andhra Pradesh, growth of NAIS was good with positive compound growth rates in terms of number of farmers insured, sum insured, gross premium and premium subsidy.. For area coverage and number of farmers benefitted, growth rates found to be negative. Results from coverage of overall crop insurance schemes found that compound growth rates were positive in all terms (Raju and Chand, 2008).
- Bio-Formulations for Plant Growth-Promoting Streptomyces SP.
- Brand Preference of Farmers for Maize Seed
- Issues That Consumer Experience Towards Online Food Delivery (Ofd) Services in Tirupati City
- Influence of High Density Planting on Yield Parameters of Super Early and Mid Early Varieties of Redgram (Cajanus Cajan (L.) Millsp.)
- Influence of Iron, Zinc and Supplemental N P K on Yield and Yield Attributes of Dry Direct Sown Rice
- Effect of Soil and Foliar Application of Nutrients on the Performance of Bold Seeded Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea L.)

