Study on Rural Consumers Buying Behaviour on Selected Fmcg Products in Krishna District
0 Views
M. SAI KIRAN*, P. GANESH KUMAR, P.V. SATYA GOPAL AND P. LAVANYA KUMARI
Institute of Agribusiness Management, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517502.
ABSTRACT
The paper entitled “Buying behavior of rural consumers towards selected Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG)” was undertaken to investigate the awareness, perception, buying pattern of rural consumers for factors like price, quality parameters, discounted offers, switching facility, packaging aspects, quantity, availability, variety, purchase experience. affecting the purchasing behavior of rural consumers and constraints faced by them while purchasing the FMCG products. Dental care, soft drinks, soaps, detergent powder, and biscuits are the products chosen for this survey. Krishna district was specifically chosen for the study because the researcher is from there. Two mandals were chosen at random from among the 53 mandals in the Krishna district. It was found that most customers are willing to purchase things from Kirana stores since it is easy for them, when compared to supermarkets, haats, and online shopping. Few customers choose to buy FMCG products from their favorite stores three times a year, with the majority choosing to do so once each month. When compared to information from friends, it was found that television is the most popular information source for purchasing FMCG products most of the villagers were having TV at their homes.
KEYWORDS: Fast Moving Consumer Goods, Rural consumers, Buying behaviour, Awareness.
INTRODUCTION
Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) or Consumer-Packaged Goods (CPG) are products that have a high shelf turnover, are generally inexpensive, and require little thought, time, or money to purchase. FMCG refers to any product that is often used, sometimes on a regular basis, and moves quickly (at least once a month) at the store level. FMCGs are all commodities that people buy on a regular basis (except food and pulses). The most regularly purchased items on the list, include toilet soaps, detergents, shampoos, toothpaste, shaving products, shoe polish, prepared meals, and domestic accessories. These items are designed to be used on a daily or regular basis and provide a high return on investment. The three main segments of the FMCG industry are personal care, food and beverages, and domestic care. The FMCG industry is primarily responsible for the manufacture, distribution, and marketing of consumer-packaged goods. The FMCG supply chain is a complex network of operations and resources. Suppliers, manufacturers, logistics service providers, warehouses, distributors, wholesalers, and all other organizations are involved in the delivery of goods to the final client are included.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The sample for the study was chosen using a random sampling procedure. Using standard random selection technique three villages from each Mandal, yielding a total of six villages and a random selection of 15 consumers from each village were done. Hence, a sample size of 90 consumers was developed. Five brands from each of the three categories of FMCG products – food and beverage (biscuits and soft drinks), oral care, and home care (toilet soaps and detergents) – will be chosen for further analysis. The survey method was used to gather the data for the current study, and pre-tested schedules were used to conduct the interviews. The period covered for the analysis was 2021–22. To achieve a set of objectives, descriptive statistics and Garrett ranking were utilized.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
STUDY ON RURAL CONSUMERS BUYING BEHAVIOUR ON SELECTED FMCG PRODUCTS
Product Preference of the rural consumer
Consumers preferences varies towards FMCG products. The Table 1 indicates the preference of FMCG products according to branded, neutral, non-branded FMCG goods by the consumers in the present study
The above Table 1 depicted that; majority of the respondents preferred to buy branded product as they are brand conscious.
Table 1. Product preference of respondents
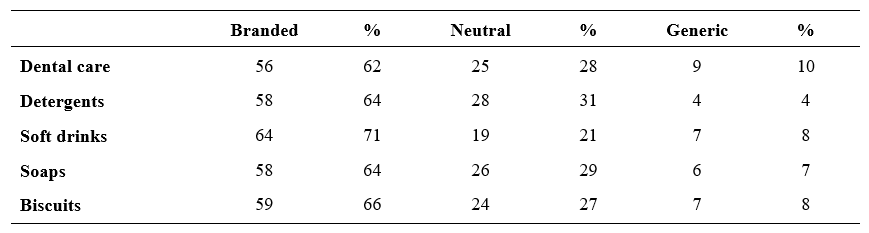
Market preference of the respondents
From the Table 2 shows that 41 per cent of respondents in the study area prefer to buy from the Kirana store, followed by 28 per cent of consumers buy from haat / mela, 21 per cent of them buy from super markets, 10 per cent buy from E-shopping. Majority of the sample respondents prefer to buy products from Kirana stores as they are convenient for them to approach
Consumer behaviour towards frequency of product purchase
According to Table 3, majority of survey respondents – roughly 71.1 percent of the overall sample size – purchase goods from their favourite stores once a month since it is more convenient for them. 13.3 per cent of all customers in the sample size made weekly purchases as their next action. Similar, 4.44 per cent of rural consumers buying things every two weeks,
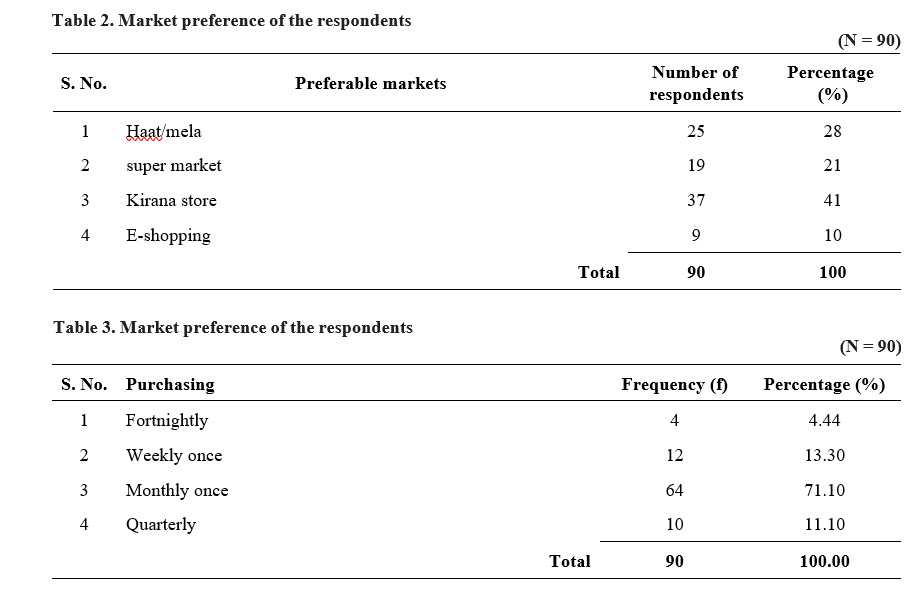
and 11.10 per cent of the total consumers buy FMCG products quarterly from their preferred stores.
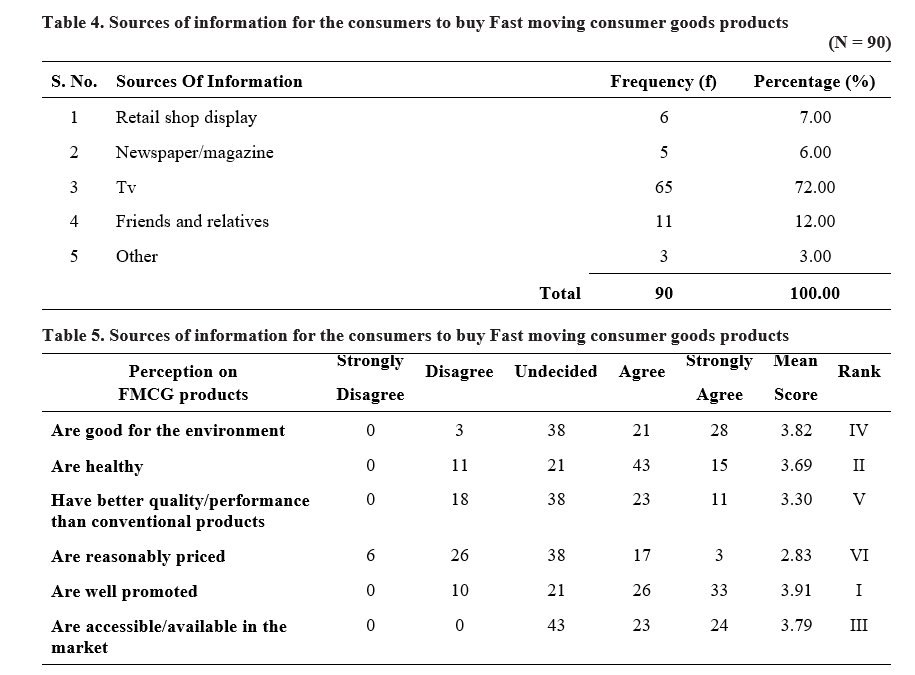
Sources of information for the consumers to buy FMCG products
Consumers purchase products after being collected information from various sources. The following table 4.11 shows the sources of information for purchase of FMCG.
Television (72%) has been identified as the popular information source for FMCG product purchases since, over time, almost all villages have installed TVs in their houses and often watch TV. The TV commercials that run in the middle of the programmes are factor influences viewers to favour products. Out of all respondents, 12 per cent acquire knowledge from friends and family, 7 per cent get it from retail store displays, 6 per cent get it from newspapers/magazines, and just 3 per cent get it from other sources.
Perception of Rural Consumers on FMCG Products
Table 5 shows that respondents from rural areas have different opinions on “fast-moving consumer goods” products. Most rural consumers strongly agree that FMCG products are well advertised and have greater brand awareness than good for the environment products, with a mean score of 3.91 compared to 3.8. With a mean score of 3.79, the majority of customers concur that they are offered in local stores, although some respondents are undecided about how easily accessible, they are and that a diversity of brands are not offered there. While many consumers think that they are healthy, a significant minority believe otherwise since chemicals are used in the production of these items, which they believe to be unhealthy. Many consumers believe that they are healthier than conventional items but are not higher quality. With a mean score of 2.86, many consumers believe that many FMCG products are overpriced.
The present study concluded that the consumers prefer to buy FMCG brands (food and beverage (biscuits and soft drinks), oral care, and home care (toilet soaps and detergents)) from kirana stores because of the easy availability. The consumer prefers specific brand as they were practiced to use that brand influence since long and thus have developed a faith on those specific product brands. Most of the consumers prefer to purchase produced brand as they were brand conscious. Majority of the consumers stick to brand for more time because they think it suits to them. The consumers purchase brands on monthly basis. With time all most all the villagers were having TV in their homes and they watch TV in their free time, so the most prominent source of information for buying FMCG brand was television.
Among the different age group young age group people were mostly likely influenced by the advertisement and attractive packing hence Advertisement was the most influencing factor while buying any FMCG brand advertisement plays major role for brand preference among rural consumers. high income group people purchasing FMCG products in higher volume when compare to low-income group
LITERATURE CITED
Agarwal, S.K. 2014. A Study of Consumer Behavior of FMCG Products in Madhya Pradesh, International Journal of Business and Management Research. 1(4): 4-5.
Ahmad, A.A.M.K. 2017. An empirical study on the behavior of rural marketing with reference to hair oils. Tactful Management Research Journal. 2(6): 136-141.
Ali, Thumki and Khan. 2012. Factors influencing purchase of FMCG by rural consumers in south India: an empirical study. International Journal of Business Research and Development. 1(1): 48-57.
Asha, K and Joy, A.M.T. 2016. Attitudinal analysis of rural consumers towards FMCG in Sivagangai district. Indian Journal of Science and Technology. 33(9): 1-5.
Awain, A.G and Ismail, Majeed, Ghazal, F. 2016. Effects of advertisement on consumer’s buying behavior with reference to FMCGs in southern Punjab- Pakistan, Journal of Marketing and Consumer Research. (19): 22-30.
Bahl, S. 2012. Brand awareness and perception of urban and rural consumers towards celebrity endorsement. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Management Studies. 1(2): 183-192.
Brosekhan, A.A and Velayutham, C. 2013. An empirical study on consumers buying behavior towards selected home appliance products in Ramanathapuram. IOSR Journal of Business and Management. 13-21.
- Bio-Formulations for Plant Growth-Promoting Streptomyces SP.
- Brand Preference of Farmers for Maize Seed
- Issues That Consumer Experience Towards Online Food Delivery (Ofd) Services in Tirupati City
- Influence of High Density Planting on Yield Parameters of Super Early and Mid Early Varieties of Redgram (Cajanus Cajan (L.) Millsp.)
- Influence of Iron, Zinc and Supplemental N P K on Yield and Yield Attributes of Dry Direct Sown Rice
- Effect of Soil and Foliar Application of Nutrients on the Performance of Bold Seeded Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea L.)

