Evaluation of Foliar Application of Nano Dap on the Performance Of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.)
0 Views
E. KUMAR*, N. SUNITHA, B. SANDHYA RANI, CH. BHARGAVA RAMI REDDY AND V. CHANDRIKA
Department of Agronomy, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517 502.
ABSTRACT
A field experiment was conducted during summer season of 2024 on sandy loam soils at Dryland Farm, S.V. Agricultural College, Tirupati campus of Acharya N.G. Ranga Agricultural University, Andhra Pradesh, India. The experiment was laid out in the randomized block design and replicated thrice. Results revealed that significantly higher growth parameters viz., plant height, leaf area index and yield attributes viz., number of capsules plant-1, number of seeds capsule-1, seed and stalk yield were recorded with application of 100% RDP + two foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS which was comparable with application of 100% RDP + one foliar spray of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS.
KEYWORDS: Growth, Phosphorus, Nano DAP, sesame, yield.
INTRODUCTION
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) commonly known as gingelly is the oldest indigenous crop cultivated as a source of quality edible oil. The nutritional value of sesame holds utmost significance for humans, as it contains 40 to 60 per cent oil, 17 to 29 per cent protein, antioxidants, dietary fibre and an array of essential minerals i.e., iron, calcium, phosphorus, zinc and magnesium. The superior nutritional, medicinal, cosmetic and cooking qualities of oil made sesame as ‘Queen of oils’. The oil is rich source of polyunsaturated fatty acids i.e. linoleic and linolenic acids bio-active compounds like sesamin, sesamolin and tocopherol, along with a stable keeping quality for a longer period.
India ranks first in world with sesame, being cultivated in area of 15.23 lakh ha with annual production of 8.02 lakh tonnes and productivity of 527 kg ha-1. It is cultivated over 0.23 lakh ha across Andhra Pradesh for food and oil, with a production of 0.07 lakh tonnes and productivity of 287 kg ha-1 during 2022-2023. (www. indiastat.com).
Phosphorus plays a vital role in the formation of energy rich phosphates bonds, nuclear protein, phospholipids and is an essential constituent of amino acids, protein, phytin and several co-enzymes. Phosphorus is necessary for the energy conversion, cell storage, early root development, flowering and seed formation (Priyadarshini et al., 2021).
Nano DAP is an effective source of nitrogen (8.0 % N w/v) and phosphorus (16.0 % P2O5 w/v). Nano DAP with an advantage in terms of surface area to volume due to the particles size less than 100 nano meter can readily enter the stomata and timely availability at critical stages for nutrition. Bio-polymers and other excipients are used to functionalize the nitrogen and phosphorus nanoclusters in nano DAP. Nano-fertilizers enhance nutrient use efficiency due to their better penetration ability and translocation within plant parts (Kopittke et al., 2019).
The present study was conducted to evaluate the performance of sesame with foliar application of nano DAP at various levels of phosphorus application.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The experiment was carried out during summer season of 2024 at S.V. Agricultural College, Tirupati campus of Acharya N.G. Ranga Agricultural University, Andhra Pradesh, India. which is geographically situated at 13.5°N latitude and 79.5°E longitude at an altitude of 182.9 m above the mean sea level in the Southern Agro-Climatic Zone of Andhra Pradesh. The soil of the experimental site was sandy loam in texture, EC (0.3 dSm-1), low in available N (147 kg ha-1), medium in available P (21.7 kg ha-1) and available K (181 kg ha-1). The Experiment was carried out in Randomized Block Design having ten treatments consisted of Phosphors levels viz., 100%, 75% and 50% and foliar spray of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1. The treatments viz., T1: Control (no application of P), T2: 100% RDP (Recommended dose of phosphorus), T3: 100% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP@ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS, T4: 100% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS, T5: 75% RDP (Recommended dose of phosphorus), T6: 75% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS, T7: 75% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP@ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS, T8: 50% RDP (Recommended dose of phosphorus), T9: 50% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP@ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS and T10: 50% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP@ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS. which were replicated thrice and the effect was observed on sarada (YLM-66) sesame variety. Sowing was done by line sowing method on 10th January 2024 with a spacing of 30 cm × 15 cm.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Growth Parameters
Plant height and leaf area index recorded varied significantly due to various levels of phosphorus and foliar sprays of nano DAP The foliar application of nano DAP in the respective treatments was carried out at 25 days after sowing. Table 1. The highest plant height and leaf area index was recorded with 100% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP@ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS (T4), which was comparable with 100% RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP@ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS which inturn was on par with 75 per cent RDP + foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS (T7) and 100 per cent RDP (T2).
The increase in plant height could partly be attributed to the combination of basal application of conventional fertilizers and foliar spraying of nano DAP as containing readily absorbable nitrogen and phosphorus which could have developed a significant increase in plant height by stimulating the plant auxin metabolism, enzyme activity of photosynthesis, carbohydrate and protein synthesis. which in turn might have prompted the cells to elongate and enlarge, ultimately leading to taller plants. The results are in close conformity with the findings of Yasser et al. (2000) and Gupta et al. (2022).
Various levels of phosphorus and foliar spray of nano DAP significantly by influenced the on leaf area index might be due to the fact that phosphorus as ATP, plays a key role in photosynthesis and is an integral part of the DNA and RNA and it also helps in development of root system. The better nitrogen and phosphorus nutrition to crop plants through foliar application also has beneficial effect on plant metabolism, which affects physiological process of the crop and there by increased the growth parameters. Nano fertilizer easily enters into leaves through stomata and other apertures, thus promoting the growth and elongation of the leaf by regulating the rate of cell division and size. Phosphorus increases leaf area and number along with acceleration of cell division by accumulating at meristematic areas.
This results were found in agreement with and Sruthy et al. (2023).
Yield attributes
The higher number of capsules plant-1 and number of seeds capsule-1 was recorded with 100 per cent RDP + foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS (T4), which was however comparable with 100 per cent RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS (T3), which was in parity with 75 per cent RDP + foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS (T7) and 100 per cent RDP (T2) (Table 2).This might be due to the fact that application of nitrogen and phosphorus in sufficient quantity might have improved the nutrient availability, leading to the increased nutrient uptake. The energy obtained from processes like photosynthesis and the breakdown of stored carbohydrates is used for growth, which ultimately leads to robust plant development. The increase in number of capsules plant-1 and number of seeds capsule-1 might be due to sufficient amount of nitrogen and phosphorus supplied through nano DAP at various stages, had maintained continuous availability of nitrogen and phosphorus leading to the active meristematic activity and stimulation of cell elongation in plants, the application of nitrogen might have exerted flower initiation and capsules formation by increasing rate of photosynthesis and transportation of assimilates from source to sink which in turn resulted in higher number of capsules plant-1 and number of seeds capsule-1. These findings are in conformity with Sujatha (2019) and Kumar et al. (2022). The lowest number of capsules plant1 and number of seeds capsule-1was obtained with the control (T1).
Yield
The highest seed and stalk yield of sesame was recorded with 100 per cent RDP + foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS (T4), which was however comparable with 100 per cent RDP + foliar spray of nano DAP @ 2ml l-1 at 25 DAS (T3), which was in turn statistically at par with 75 per cent RDP + foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS
Table 1. Plant height and Leaf area index of sesame as influenced by various levels of phosphorus and foliar application of nano DAP
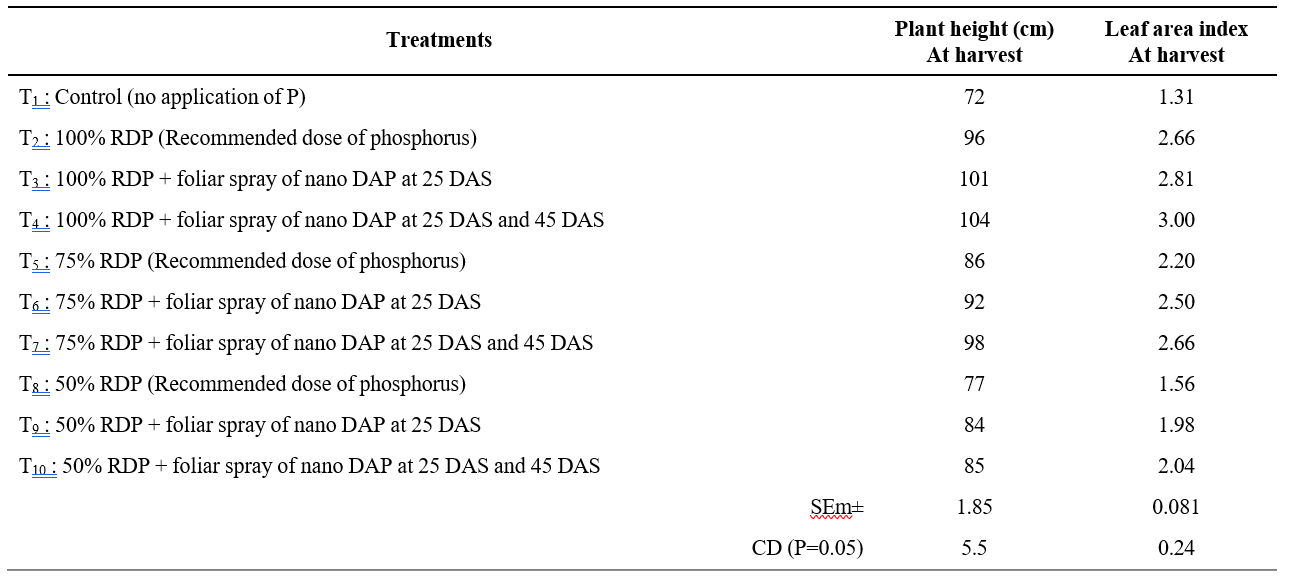
Table 2. Yield attributes and yield of sesame as influenced by various levels of phosphorus and foliar application of nano DAP
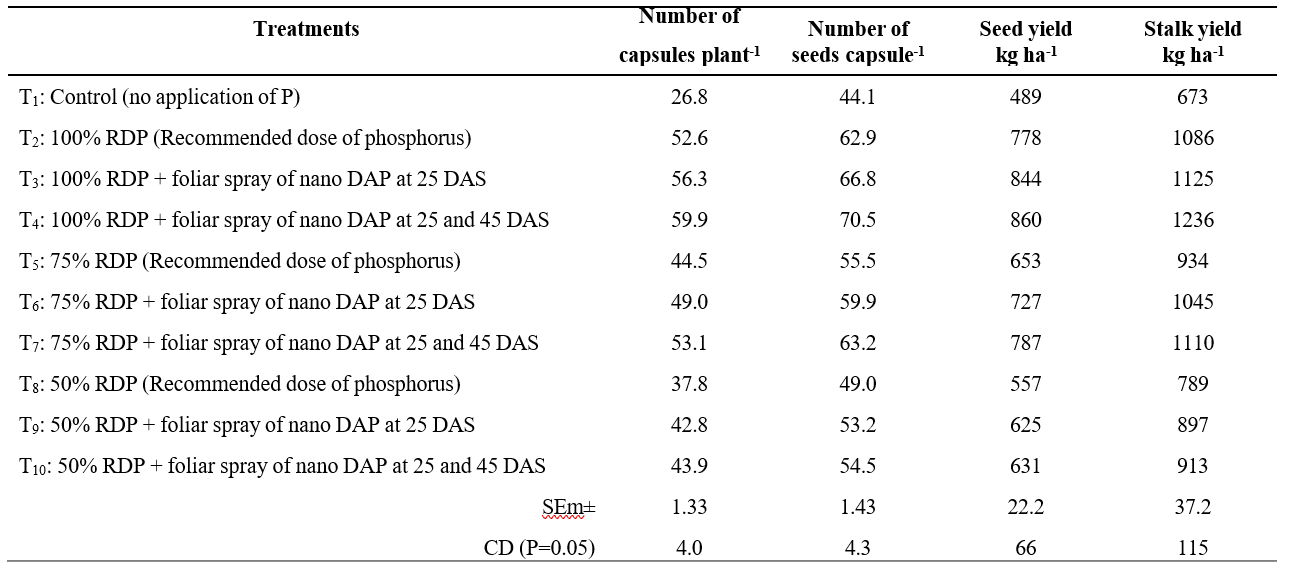
(T7) and 100 per cent RDP (T2).This might be due to the better performance of crop growth with timely supply of adequate quantity of required plant nutrients in a balanced proportion. The increase in seed yield can be attributed to the effective metabolic activities coupled with increased rate of photosynthesis, leading to better translocation of nutrients and expression of developmental characters. The foliar application of DAP twice at 25 and 45 DAS might have met out N and P requirement at the critical stages of the crop due to ensured and prompt delivery of mineral nutrients to the site of photosynthesis in leaves. Further nutrients applied through foliage would be easily available and translocated in the plants without any loss. More grain yield was obtained due to timely supply of nitrogen and phosphorus through soil application and also supplemented with foliar nutrition which helped in the development of strong and highly dense shoot and root system enabling better absorption of essential nutrients from the soil solution. Similar findings were in relation with Pandav et al. (2022).
Higher stalk yield might be due to the pronounced role of soil application of phosphorus and foliar application of nano DAP to supply nitrogen and phosphorus which plays a crucial role in enhanced photosynthesis and further cell multiplication with production of higher number of branches and leaves, that ultimately increased dry matter production as reflected in the form of higher stalk yields. Nutrient supply through combination of soil application of conventional and foliar spray of nano fertilizers meet crop nutrient demand and increased the rate of photosynthesis for a longer period even at later stages and thus accumulation of dry matter directly resulted in a higher stalk yield. The results are in agreement with the findings of Mallikarjuna (2021) and Rajput et al. (2022).
In conclusion, it is revealed that soil application of 100 per cent recommended dose of phosphorus @ 20 kg ha-1 in combination with two foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 and 45 DAS could be the best phosphorus management practice for obtaining higher productivity and economic returns of sesame, however it was at par with 100 per cent RDP + foliar sprays of nano DAP @ 2 ml l-1 at 25 DAS on sandy loam soils of Southern Agro- Climatic Zone of Andhra Pradesh.
LITERATURE CITED
Gupta, S.P., Mohapatra, S., Mishra, J., Yadav, S.K., Verma, S and Singh S. 2022. Effect of nano nutrient on growth attributes, yield, Zn content, and uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). International Journal of Environment and Climate Change. 12(11): 2028- 2036.
Kopittke, P.M., Lombi, E., Wang, P., Schjoerring, J.K and Husted, S. 2019. Nano materials as fertilizers for improving plant mineral nutrition and environmental outcomes. Environmental Science. 6(12): 3513-3524.
Kumar, N., Chovatia, P.K., Kumar, S., Deshmukh, A and Agarwal, D. 2022. Effect of foliar application of NPK and micronutrients on growth, yield and quality parameters of summer sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). The Pharma Innovation Journal. 11(7): 153-156.
Mallikarjuna, P.R. 2021. Effect of nano nitrogen and nano zinc nutrition on nutrient uptake, growth and yield of irrigated maize during summer in the southern transition zone of Karnataka. M.Sc. (Agri.) Thesis. Keladi Shivappa Nayaka University of Agricultural Sciences, Shivmogga.
Pandav, D.M., Talathi, M.S., Bodake, P.S., Chavan, V.G., More, S.S., Pethe, U.B., Rajemahadik, V.A., Ghodake, S.S and Mote, G.K. 2022. Response of nitrogen level and nano urea on mustard (Brassica juncea L.) under Konkan condition. The Pharma Innovation Journal. 11(12): 2055-2061.
Priyadarshini, A., Umesha, C and Meshram, M.R. 2021. Influence of phosphorus and potassium levels on growth, yield and economics of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) under eastern Uttar Pradesh condition. Biological Forum – An International Journal. 13(1): 645-650.
Rajput, J.S., Thakur, A.K., Nag, N.K., Chandrakar, T and Singh, D.P. 2022. Effect of nano fertilizer in relation to growth, yield and economics of little millet (Panicum sumatrense L.) under rainfed conditions. The Pharma Innovation Journal. 11(7): 153-156.
Sruthy, H., Pillai, P.S., Shimi, G.J., Bindhu, J.S and Sajeena, A. 2023. Growth and yield of grain cowpea (Vigna unguiculata sub sp. Cylindrica) in response to foliar nutrition and graded levels of phosphorus and potassium. International Journal of Environment and Climate Change. 13(11): 4001-4014.
Sujatha, S.V. 2019. Effect of foliar nutrition of nitrogen and potash on seed yield and economics of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) in North Coastal zone of Andhra Pradesh. International Journal of Chemical Studies. 7(6): 138-140.
Yasser, E.E., El-Ghobashy, Elmehy, K.A and El-Douby, K.A. 2000. Influence of intercropping cowpea with some maize hybrids and N nano mineral fertilization on productivity in salinity soil. Egyptian Journal Agronomy. 42(1): 63-78.
- Effect of Sowing Window on Nodulation, Yield and Post – Harvest Soil Nutrient Status Under Varied Crop Geometries in Short Duration Pigeonpea (Cajanus Cajan L.)
- Nanotechnology and Its Role in Seed Technology
- Challenges Faced by Agri Startups in Andhra Pradesh
- Constraints of Chcs as Perceived by Farmers in Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh
- Growth, Yield Attributes and Yield of Fingermillet (Eleusine Coracana L. Gaertn.) as Influenced by Different Levels of Fertilizers and Liquid Biofertilizers
- Consumers’ Buying Behaviour Towards Organic Foods in Retail Outlets of Ananthapuramu City, Andhra Pradesh

