Dus Testing of Sesame (Sesamum Indicum L.) Accessions Using Morphological Descriptors
0 Views
B. NARAYANA REDDY*, D. BHARATHI, B. RUPESH KUMAR REDDY, G. MOHAN NAIDU AND B. SANTHOSH KUMAR NAIK
Department of Seed Science and Technology, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517 502.
ABSTRACT
The aim of the present study is to assess 100 sesame genotypes based on DUS descriptors. The experiment was conducted in Alpha Lattice Design with two replications at Regional Agricultural Research Station, Tirupati during rabi 2024-25. Based on the results of frequency distribution, a majority of sesame accessions were found to possess medium duration of 50% flowering with light purple petal colour, dense petal hairiness, medium plant branching, medium plant height, basal branching pattern, absent stem hairiness, medium leaf size, slightly lobed leaf, strong leaf serration, absent capsule hairiness, four locules per leaf axil, narrow oblong capsule shape, one capsule per leaf axil, alternate capsule arrangement, medium maturity, medium thousand seed weight, white seed coat colour and low oil content percent. The study highlights distinct morphological variations among sesame genotypes due to genetic differences, offering valuable insights for breeders in varietal selection, identification, and conservation.
KEYWORDS: DUS testing, Sesame
INTRODUCTION
Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.), a member of the order Tubiflorae belongs to family Pedaliaceae is an ancient oil seed known to humankind. Sesame seeds have been widely employed in culinary as well as in traditional medicines for their nutritive, preventive, and curative properties. Owing to its high quality, sesame is also referred to as the “Queen of oil seed crops” because it contains high oil (38- 54%), protein (18 25%), calcium, phosphorous, oxalic acid and excellent qualities of seed oil and meal. important pre requisites for effective utilization of germplasm and also to identify sources of useful genes (Manasa et al., 2025). Identification of genotypes based on morphological characteristics of seed, seedling and plant is the most widely used method. According to International Union for Protection of New Plant Varieties (UPOV), any new characteristic used in varietal characterization should be clearly defined, accepted and should have standard method of observation, least or not affected by environment, accessible to breeders, associated with reasonable costs and efforts (Bhoot et al., 2019).
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The present investigation was carried out in Regional Agricultural Research Staton, Tirupati during rabi 2024-2025 with 100 genotypes evaluated in two replications using Alpha Lattice Design. Each genotype was sown in two rows in three meters length. The recommended agronomical practices and plant protection measures were followed for raising successful crop. DUS characterization was done as per the guidelines developed by PPV & FR act, India. Observations were recorded on twenty DUS descriptors viz., days to 50% flowering, petal colour, petal hairiness, height of the stem (cm), branching, branching pattern, stem hairiness, leaf lobes, leaf size, leaf serration, capsule hairiness, locules per capsule, capsule shape, capsule per axil, capsule arrangement, capsule length (cm), days to maturity, seed coat colour, test weight and oil content.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
DUS descriptors were used to analyze the 100 genotypes for morphological characteristics of the sesame cultivars. The findings revealed variation among the all characters. The results for each trait are described briefly presented in Table 1.
Similar findings was reported by Singh et al., (2017), Pavani et al., (2020), Vanishree (2021) and Manasa et al., (2025) also exploited this trait during their studies on characterization of sesame genotypes.
Table 1. Morphological characterization of genotypes for descriptor exhibition with frequency.
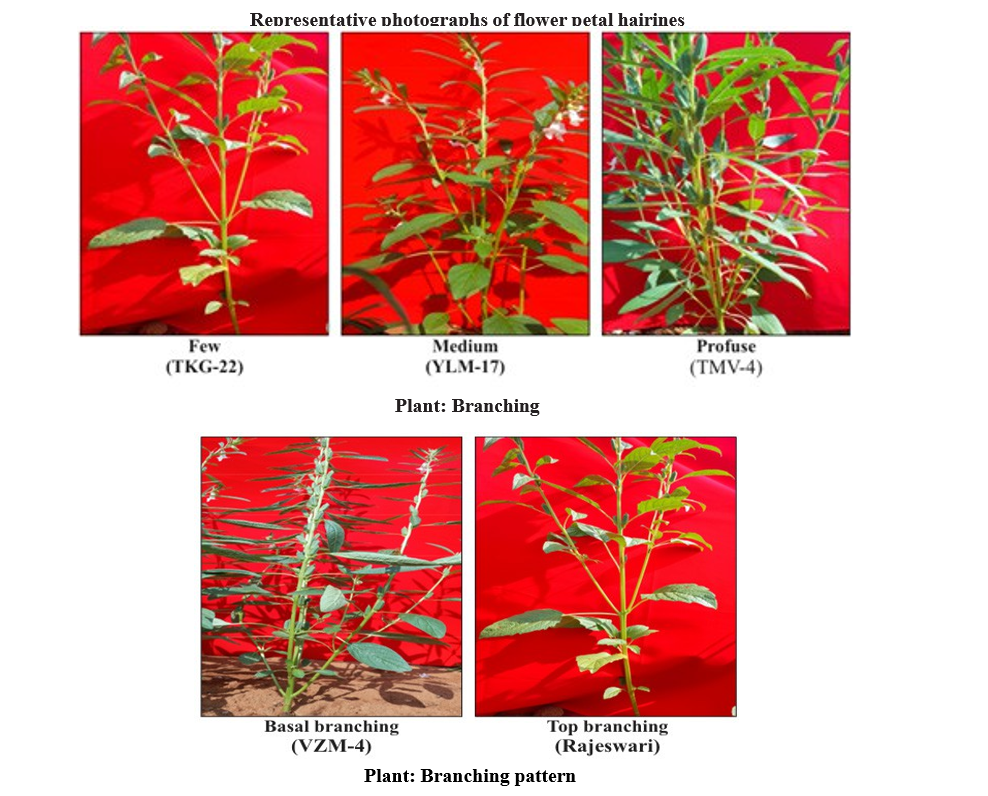

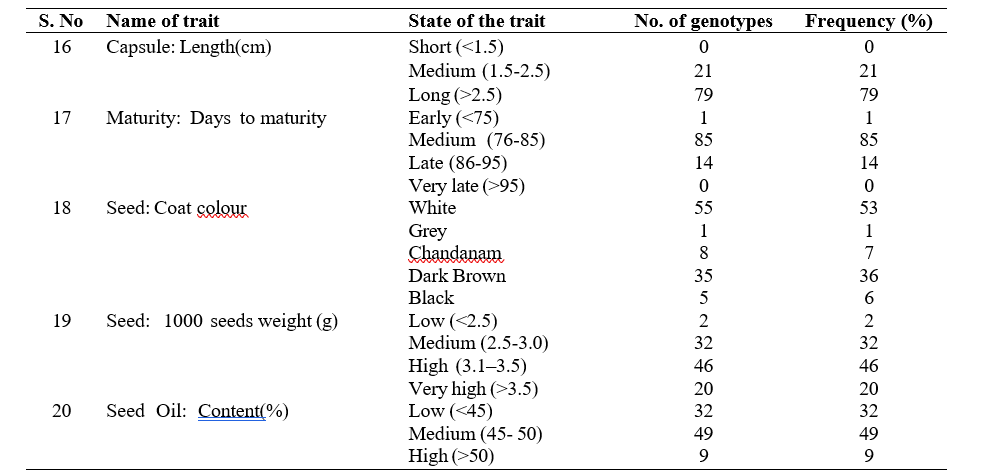



Based on the above results, it could be concluded that characterization of 100 sesame genotypes based on morphological characterization during rabi season revealed that considerable variation in key traits, offering valuable insights for varietal identification and crop improvement.
LITERATURE CITED
Bhoot, H.V., Sharma, L.K., Kulkarni, G.U., Ravat, U and Rathva, S. 2019. Characterization of sesame genotypes through morphological characters. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry. 8(3): 3132-3138.
Manasa, A., Bharathi, D., Veeraghattapu, R., Mallapuram, S.P., Padherla, L.K., Vulusala, B.P., Gangireddy, A.K., Killada, G.K., SaiVenkat, K.S. and Vemieddy, L.R., 2025. Development of QR codes for rapid identification of sesame cultivars using DUS descriptors and molecular markers. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, pp.1-20.
Pavani, K., Lal Ahamed, M., Ramana, J.V and Sirisha, A.B.M., 2020. Studies on genetic variability parameters in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). International Journal of Chemical Studies. 8(4): 101-104.
PPV&FRA (2007). Guidelines for the conduct of test for distinctiveness, uniformity and stability on sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Authority, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India.
Singh, B., Bisen, R. and Tiwari, A., 2017. DUS testing of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) varieties using morphological descriptors. Bull Environ Pharmacol Life Science, 6(1), :05-12.
Vanishree, S.G., Banu, H., Palakshappa, M.G and Holeyannavar, P. 2022. Morphological characterization of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) germplasm accessions with DUS. The Pharma Innovation Journal 2022; 11(12): 938-945.
- Effect of Sowing Window on Nodulation, Yield and Post – Harvest Soil Nutrient Status Under Varied Crop Geometries in Short Duration Pigeonpea (Cajanus Cajan L.)
- Nanotechnology and Its Role in Seed Technology
- Challenges Faced by Agri Startups in Andhra Pradesh
- Constraints of Chcs as Perceived by Farmers in Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh
- Growth, Yield Attributes and Yield of Fingermillet (Eleusine Coracana L. Gaertn.) as Influenced by Different Levels of Fertilizers and Liquid Biofertilizers
- Consumers’ Buying Behaviour Towards Organic Foods in Retail Outlets of Ananthapuramu City, Andhra Pradesh

