A Study on Constraints Faced by Consumer While Buying Organic Food Products in Bangalore
0 Views
RAVI KALYANI*, A. VISHNUVARDHAN REDDY, Y. PRABHAVATHI AND P. LAVANYA KUMARI
Institute of Agribusiness Management, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517 502.
ABSTRACT
The aim of the current study was to determine the constraints faced by consumer while buying organic food products. This study was purposively conducted in Bangalore district of Karnataka and ex-post facto research design was followed for the study. Major six organic retail stores were randomly chosen for the study. Twenty consumers visiting each organic retail store were selected randomly thus the total sample size was 120. The data pertaining to constraints of consumers for buying organic food products were collected by personally interviewing the respondents using a pre-structured schedule. Statistical tool like Garret ranking technique were employed to analyze the data. The empirical findings of the study revealed that the majority of the constraints faced by consumer while buying organic food was the products are expensive followed by limited choice in organic food products range.
KEYWORDS: Constraints, Consumers, Organic, Food products.
INTRODUCTION
Introduction of the High yielding varieties (HYV) through the green revolution in 1960’s was leading to the usage of more amounts of the inorganic (chemical) fertilizers and pesticides for crop production, due course of time the over or indiscriminate use of these inorganic compounds leading to the health hazards and environmental effects. So, in order to maintain the balance with the environment and sustainability of agriculture it is necessary to reduce the usage of inorganic chemical compounds and increase the use of organic based pesticides and products for cultivation of crops. The growing of the crops without usage of the inorganic (chemical) compounds is called organic farming. Organic farming in India was evolved in about 4000 years ago, traditional farming in India was part of our great Indian civilization. Campaigns such as grow more food (1940s) and Integrated Production Programme (IPP) (1950s) focused on the food and cash crops supply respectively. Organic food products are expected to reach US$ 4602 million by 2028, up from US$ 1278 million in 2022, with a CAGR of 23.8%. (IMARC). According to the data India ranks first in terms of the number of producers and fifth in terms of total amount of land used for organic agriculture worldwide. (Book by FiBL & IFOAM, 2023). The total area under organic certification as on March 31, 2022, according to the National Program for Organic Agriculture, is 9119865.91 hectares and around 3430735.65 metric tons of certified organic products, including all types of food products, were produced in India in 2021–2022. (APEDA, 2021-2022). The demand for organic food materials or organically derived foods was increasing day by day and is quickly expanding nature ensures a significant profitable venture in the future. The consumption of these organic foods and drinks has increased in the past few years due to its awareness and information, economic growth, higher purchasing power and growing interest among the people. Consumption of these organic foods gives good health and resistance which can combat the lifestyle disease in comparison with the conventionally cultivated foods which destroying the health due to its pesticide hazardous nature etc. As the demand for organic items continues to grow, businesses must adapt their marketing strategies to effectively target and engage with the conscious consumer. So, through this research, we aim to gain valuable insights into the constraints faced by consumers buying organic food products. By doing so, we can recognize the actual barriers to organic food product penetration into the market.
METHODOLOGY
The study was conducted at Bengaluru which is divided into Bangalore urban, Bangalore rural. The data collection is carried out in Bangalore urban city of Karnataka during the year 2023 and ex-post facto research design was followed for the study. From the selected city,
major six organic retail stores were randomly chosen for the study. Twenty consumers visiting each organic retail store were selected randomly thus the total sample size was 120. This study aims to examine the constraints faced by consumers while buying organic food products to provide valuable insights into the barriers to organic food products penetration into the market and the consumer constraints that companies need to focus on. Based on exhaustive review of literature, interaction with organic food products consumers and by taking expert’s opinion, a total of 10 statements were listed and consumers were asked to rank their opinions on these statements The constraints were prioritized by adopting Garret ranking technique. Suggestion was operationally defined as the requirements expressed by the organic food product consumers in order to fulfill their needs.
Garrett’s Ranking Technique
To find out the major constraint faced by the respondent; Garrett’s ranking technique was used. The prime advantage of this technique over simple frequency distribution is that the constraints are arranged based on their severity from the point of view of respondents. Hence, the same number of respondents on two or more constraints may have been given different rank.
Garr ett’s formula for converting ranks into percent is:
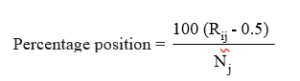
where Nj
Rij= Rank given for ith statement by jth consumer.
Nj = Total number of constraints ranked
With the help of Garrett’s table, the percent position estimated is converted into scores. Then for each constraint, the scores of each individual are added and then the total value of scores and mean values of score is calculated. The constraints having the highest mean value is considered to be the major constraint. The final ranking of the constraints in order to fix their relative priority was done on the basis of their mean score
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Constraints in buying organic food products by sample consumers:
Information of opinion on constraints in purchasing of organic food products was collected by using 10 statements. Then the opinion of the sample consumers was analyzed using a garrett’s ranking method, with the least considered statement ranked as ten (10) and the most
considered statement ranked as one (1), respectively. The scores got for each identified parameter were summated, and the respective garrett’s mean score were estimated and are arranged in descending order as per the garret mean score and given the ranks.
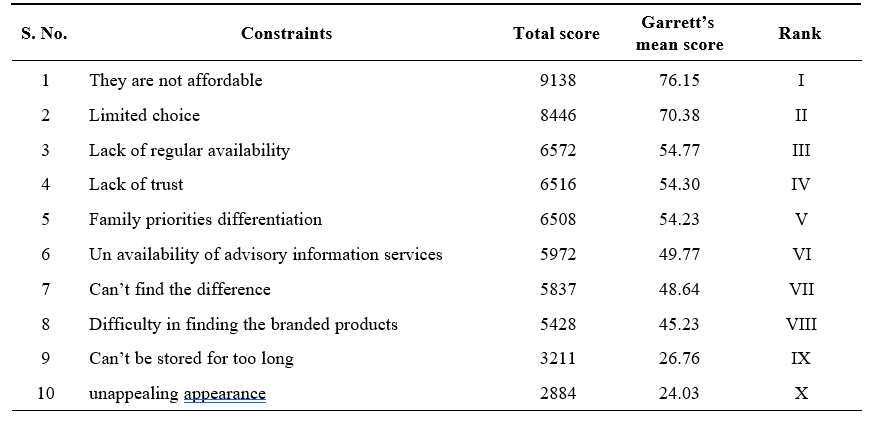
The results of Table 1 indicated that the major constrain while facing the organic food product is the products being not in affordable range with the garrett’s mean score of 76.15, followed with limited choice, lack of regular availability, lack of trust, family priorities differentiation, un availability of advisory information services, can’t find the difference, Difficulty in finding the branded products, Can’t be stored for too long are the other constraints with mean scores, 70.383, 54.767, 54.3, 54.233, 49.767, 48.642, 45.233, 26.758. The least ranked
parameter is unappealing appearance with garrett’s mean score 24.033. Thus, organic food being expensive is the major constrain and the unappealing appearance is the least constrain faced by sample consumers in buying organic food.
SUGGESTIONS
- Addressing expensive perceptions: The premium price range is the major hindrance to buying organic food So, by promoting the benefits of their consumption in the long term and communicating the value organic foods create for them in return for their high price, transparent pricing, i.e., letting them witness how their money creates an impact at the root level, will help to clear the mark of expensive products and value them as a way of healthy lifestyle products.
- Family-friendly options: The current scenario of the household has created a surge of ready-to-go meals. So, it is good to create easy, healthy snacking options, easy-to-prepare meals and many healthy on-the-go options that cater to the needs of all generations.
- Diversity in product range: With the available options, one cannot have a complete set of organic food products. So, increase the range of products offered to cater to diverse consumer preferences. Along with the product range, make them regularly available, which will help reduce shifts in
- Traceability: Now-a-days loyalty is becoming a major concern due to the availability of many other So, by introducing traceability, you can build trust among customers about the journey your products went through and the credibility of certification, which will play a major role in building loyalty among customers about the brand.
Table 1. Constraints in purchasing of organic food products
- Promotion: The major market stimuli for communication are word of mouth, television, and social media, mainly through influencers. The major motives for purchasing organic food products are health benefits and food safety concerns. So, communication needs to be done through them with these motives.
In conclusion, the article has examined the significant constraints faced by the organic food products consumers while buying them and majority of them are organic food products as expensive, having limited choice, lack of regular availability, differences in the family priorities. Thus, to overcome these constraints effective strategies like addressing expensive perceptions, family- friendly options, diversity in product range, traceability, promotion will be helpful.
LITERATURE CITED
Buder, F., Feldmann, C., Hamm, U and Hempel, C. (2014). Why regular buyers of organic food still buy many conventional products Product-specific purchase barriers for organic food consumers. British Food Journal. 116: 390-404.
Ham, M., Pap, A and Bilandžić, Ka. 2016. Perceived barriers for buying organic food products. Niedermeier, A., Emberger-Klein, A and Menrad, 2020. Drivers and barriers for purchasing green Fast-Moving Consumer Goods: A study of consumer preferences of glue sticks in Germany. Journal of Cleaner Production. 30(4): 1823-1838.
Putri, A and Nuraeni, S. 2021. Study of barriers in purchasing organic clothing product among z generation women in indonesia. Malaysian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities (MJSSH). 6(9): 564-565.
Sandhu, Y. 2022. An exploratory investigation of consumer motives and impeding barriers to buying organic food products in pakistan. 11: 128-136.
Wijaya, T., Utama, A., Mustikasari, A and Sholikhah, Z and Sinnappan, P. 2022. Motives and barriers of organic food consumption behaviour: a comparative study between Indonesia and Malaysia. International Journal of Green Economics 16(1): 1-17.
- Genetic Divergence Studies for Yield and Its Component Traits in Groundnut (Arachis Hypogaea L.)
- Correlation and Path Coefficient Analysis Among Early Clones Of Sugarcane (Saccharum Spp.)
- Character Association and Path Coefficient Analysis in Tomato (Solanum Lycopersicum L.)
- Survey on the Incidence of Sesame Leafhopper and Phyllody in Major Growing Districts of Southern Zone of Andhra Pradesh, India
- Effect of Organic Manures, Chemical and Biofertilizers on Potassium Use Efficiency in Groundnut
- A Study on Growth Pattern of Red Chilli in India and Andhra Pradesh

