Optimizing Phosphorus Nutrition in Groundnut Through Nano Dap Based Foliar Feeding
0 Views
J. KRUPA AMRUTHA*, D. SAMPATH KUMAR, A.V. NAGAVANI , G. P. LEELAVATHY AND V. CHANDRIKA
Department of Agronomy, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517 502.
ABSTRACT
A field experiment was conducted at Agricultural Research Station, Kadiri, during Rabi, 2024-25 to evaluate the effect of nano DAP on the growth and yield of groundnut. The experiment consists of 50% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T1), 50% recommended dose of P2O5 + Two sprays of Nano-DAP at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T2), 75% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T3), 75% recommended dose of P2O5 + Two sprays of Nano-DAP at 30-35 and 50 -55 DAS (T4), 100% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T5), 100% recommended dose of P2O5 + Two sprays of Nano-DAP at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T6), Foliar application of Nano-DAP @2.5 ml l -1 twice at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T7), 100% RDP ( 40 kg P2O5 ha-1), (T8) and Absolute control (T9). This experiment was laid out in RBD with nine treatments and three replications. Various levels of nano DAP treatments were evaluated. Among the tested treatments application of 100% recommended dose of P2O5 along with two sprays of Nano-DAP@ 2.5 ml l-1 at 30- 35 and 50-55 DAS (T6) recorded Significantly higher plant height, leaf area index, dry matter production and yield attributes pod and haulm yield. The results indicates that improved phosphorus availability and uptake efficiency due to the synergistic effect of soil-applied phosphorus and foliar-feed nano DAP. The nano form of DAP likely ensured better nutrient absorption through the foliage, reduced nutrient losses and enhanced physiological activity, contributing to better vegetative growth and reproductive development.
KEYWORDS: Foliar nutrition, nano DAP, groundnut.
INTRODUCTION
Groundnut is the king of vegetable oilseed crops. It is the 4th most important source of edible oil and 3rd most important source of vegetable protein in India. It is a versatile legume oil seed crop, belong to Leguminaceae family and originated in Brazil. Groundnut plays an important role in meeting the demand of edible oil across the world and is popularly named as monkey nut, earth nut, unpredictable legume and energy capsule. India is the top producing nation in the world accounting to about 39.3 % area, with 27.3 % production. In India it is cultivated over 4.9 m ha in India, with a production of 9.25 m ha and with an average productivity of 1893 kg ha-1. Andhra Pradesh produces around 0.6 million tonnes from an area of 0.59 million ha, with productivity of 1011 kg ha-1(Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Andhra Pradesh, 2022-2023). Groundnut seed contains 47-50% oil, 26% protein and 11.5 % of starch (Noubissié et al. 2012). Groundnut oil, valued for its sweet flavour, is commonly used in cooking and to improve groundnut yield and quality the use of nano DAP has shown great potential. Nano DAP supplies essential nutrients nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in nano-sized particles, which enables more efficient absorption and utilization by plant cells through foliar application. Unlike conventional DAP, nano DAP ensures precise and efficient nutrient delivery, minimizing losses caused by leaching, fixation or volatilization. When applied during key growth stages nano DAP significantly enhances photosynthesis, root growth, and flowering, thereby promoting healthier plants and improved crop productivity. This experiment was conducted with a focus on improving soil health by minimizing excessive chemical fertilizer inputs and enhancing nutrient balance in the cropping system. The use of nano DAP, due to its higher efficiency and lower application rate helps to reduce the environmental footprint of phosphorus fertilization particularly by mitigating the risk of eutrophication of water bodies caused by phosphorus runoff. Additionally, the improved nutrient use efficiency leads to cost savings for farmers and contributes to the reduction of soil and environmental pollution, supporting the goals of sustainable agriculture.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Experimental Details Experimental site
The experiment was conducted at the Agricultural Research Station, Kadiri during Rabi, 2024- 25. The soils of the experimental site are sandy loam in texture, neutral pH (7.0) and non-saline (EC: 0.42 dSm-1), low in organic carbon (0.27 %) and available nitrogen (206.62 kg ha-1), medium in available phosphorus (36.5 kg ha-1) and potassium (232.15 kg K2O ha-1).
plant height at harvest compared to other treatments tried (Table 1). The significant variation in plant height across treatments indicates that phosphorus, particularly when supplemented with foliar application of nano DAP, promotes early vegetative growth. The increase in plant height can be attributed to the role of phosphorus in enhancing cell division and cell expansion, along with stimulation of biological activity of photosynthetic pigments and enzymes, thereby improving biomass accumulation and potentially contributing to better yield attributes. Similar observations were recorded by Chinnappa et al. (2023). The absolute control (T9)
Statistical analysis of results
The field experiment was conducted in a Randomized Block Design (RBD) involving nine treatments and three replications with a plot size of 4.5 m × 5.0 m. The collected data were statistically analysed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA)for Randomized Block Design as suggested by Panse and Sukhatme (1985). Statistical significance was tested with ‘F’ value at five per cent level of probability. Critical difference (CD) for the significant source of variation was calculated at five per cent level of significance. The treatmental differences those were non-significant were denoted by “NS”. The treatments consisted of 50% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T1), 50% recommended dose of P2O5 + Two sprays of Nano-DAP at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T2), 75% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T3), 75% recommended dose of P2O5 + Two sprays of Nano-DAP at 30-35 and 50 -55 DAS (T4), 100% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T5), 100% recommended dose of P2O5 + Two sprays of Nano- DAP at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T6), Foliar application of Nano-DAP @ 2.5 ml l -1 twice at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T7), 100% RDP ( 40 kg P2O5 ha -1), (T8) and Absolute control (T9). Recommended dose of fertilizer (30:40:50 kg of N: P2O5: K2O ha -1). Seeds of groundnut (Kadiri -6) were sown in 22.5 × 10.0 cm spacing with ridge and furrow method.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Growth Attributes Plant height (cm)
P2O5 along with two foliar sprays of nano DAP 2.5 ml l-1 at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T6) recorded maximum noticed shortest plants of groundnut at harvest.
Leaf area index
The leaf area index (Table 1) was recorded higher with the application 100 % recommended P2O5 along with two foliar sprays of nano DAP 2.5 ml l-1 at 30- 35 and 50-55 DAS (T6) at harvest and however it was on par with application of 100% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T5). Due to a combination of enhanced nutrient uptake, improved root and leaf development, better photosynthesis, and increased plant resilience can be observed. The efficient and sustained nutrient release provided by nano-DAP, along with other nutrients provides plants with the resources they need to expand their leaf area, which in turn supports greater photosynthetic capacity and overall plant productivity. Basal fertilizer to the soil and as foliar application had a positive influence on leaf area index. Similar findings were observed with Mahachandramuki et al. (2023). The absolute control (T9) noticed a minimum leaf area index at harvest.
Dry matter accumulation
Dry matter accumulation was higher (Table 1) with application of 100% recommended P2O5 along with two foliar sprays of nano DAP 2.5 ml l-1 at 30-35 and 50- 55 DAS (T6) was on par with 100% recommended dose of P2O5 + One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T5) Significant increase in dry matter was due to increased photosynthesis, which transforms sunlight, CO2 and water into glucose and other key compounds that boost overall biomass.
Nano fertilizers results in better absorption of nano nutrients and photosynthetic activity. Both will enhance vegetative growth due to proper supply of nutrients and accumulation of dry matter in leaves, the photosynthetic
Table 1. Growth parameters of groundnut as influenced by different levels of phosphorus and nano DAP
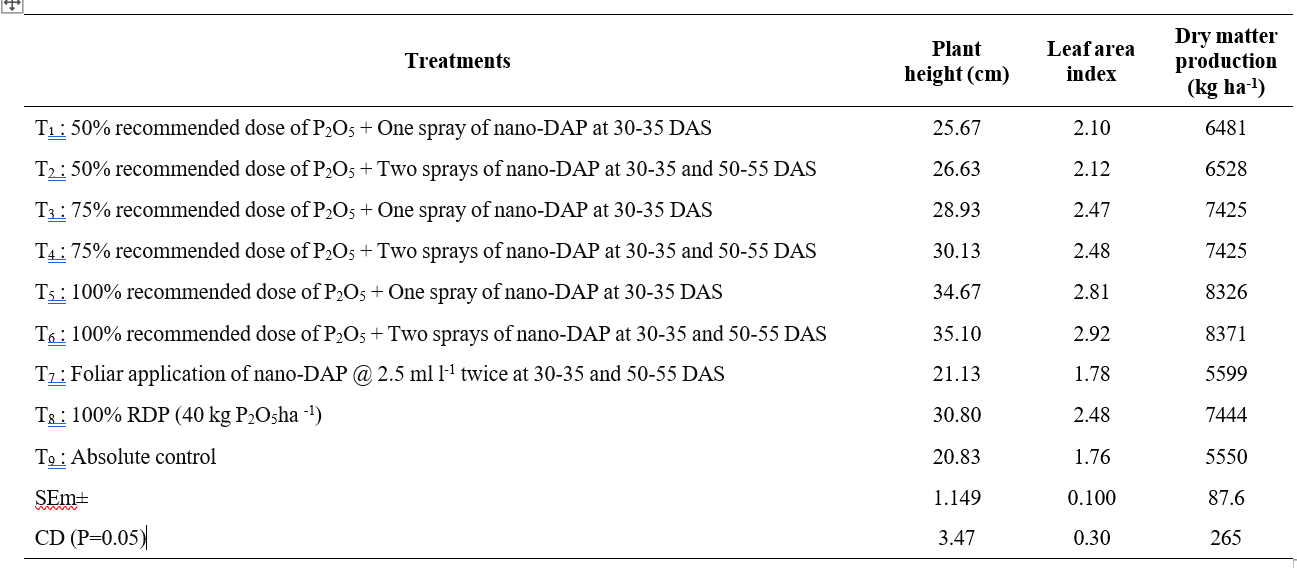
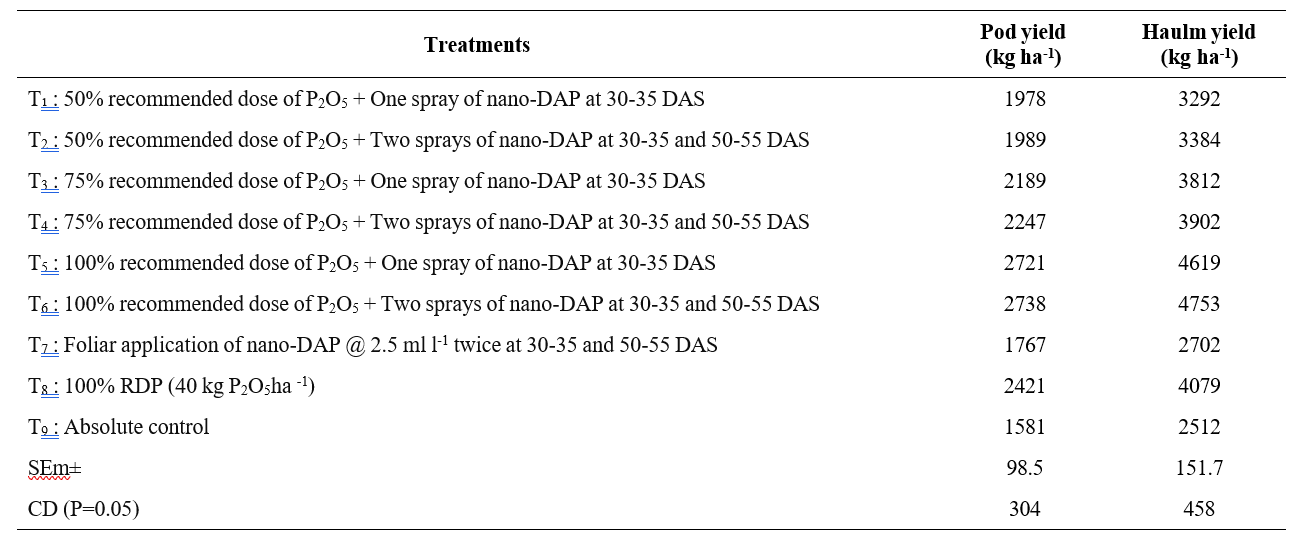
Table 2. Pod yield and haulm yield of groundnut as influenced by different levels of phosphorus and nano DAP
area remains active for longer period and was responsible for growth of plant in terms of dry matter. Application of nutrients in combination increased the supply of required required nutrients for growth and development which resulted in higher dry matter accumulation in the reproductive parts and formation of higher sink capacity. Nano DAP was helpful for efficient nutrient transportation that enhances nutrient availability directly to plant tissues, promoting better growth (Khandare et al., 2024). The absolute control (T9) noticed least dry matter production at harvest.
Yield Attributes Pod yield (kg ha-1)
Response of nano DAP has significant effect on pod and kernel yield of groundnut (Table 2). Higher pod and haulm yield (2738 and 4753 kg ha-1) of groundnut was recorded with application of 100 % recommended dose of P2O5 along with two foliar sprays of nano DAP 2.5 ml l-1 at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T6), which was comparable with application of 100% recommended dose of P2O5
+ One spray of Nano-DAP at 30-35 DAS (T5). The increase in pod yield of groundnut with phosphorus and nano DAP application might be due to enhanced nutrient use efficiency, improved root and shoot growth, better flowering and pod formation and overall healthier plant development. Nano DAP boosts phosphorus availability and uptake, leading to better yields with lower input costs and supports optimal growth and metabolic processes such as photosynthesis which promotes the accumulation and translocation of photosynthates to the plant economic parts, resulting in higher yields and better translocation of assimilates to the reproductive parts leds to higher pod yield. Similar results were reported by Sagar et al. (2021). The absolute control (T9) recorded lower pod yield of groundnut.
Haulm yield (kg ha-1)
Among the various treatments evaluated (Table 2) Application of 100 % recommended P2O5 along with two foliar sprays of nano DAP 2.5 ml l-1 at 30-35 and 50-55 DAS (T6) recorded higher haulm yield of groundnut which was comparable with 100% recommended dose of P₂O₅ along with one foliar spray of nano DAP at 30–35 DAS (T₅). The positive effects of phosphorus and nano DAP on haulm yield might be due to pronounced role of nitrogen and phosphorus in cell elongation and photosynthesis leds to higher growth parameters and higher haulm yield.
Similar findings were reported with Rajput et al. (2022) and Mallikarjuna (2021). The application of nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus through foliar nutrition may boost protoplasmic components, which are crucial for physiological processes like chlorophyll and protein synthesis, ultimately leading to increase in haulm yield. The lowest haulm yield was recorded with absolute control (T9) due to limited availability of nutrients.
Application of 100% recommended dose of P₂O₅ as basal combined with two foliar sprays of Nano DAP @ 2.5 ml l-1 at 30-35 and 50–55 days enhanced the plant height, leaf area index and dry matter production. Significantly higher pod yield and haul yield was recorded with same treatment. By improving efficiency and sustainability, nano DAP aligns with modern agricultural goals and offers a pathway toward more productive and eco- friendly farming systems.
LITERATURE CITED
Chinnappa, S.A., Krishnamurthy, D., Ajayakumar, M.Y., Ramesha, Y.M and Ravi, S. 2023. Response of Nano fertilizers on growth, yield and economics of kharif sorghum. The Pharma Innovation Journal. 12(9): 761-765.
Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Planning Department, Government of Andhra Pradesh. 2022- 2023. Agricultural statistics at a glance.
Khandare, V.P., Gaikwad, G.K., Ugile, S.K., Dhembare, N.P and Labade, P.D. 2024. Effect of foliar application of nano urea, nano DAP and growth regulator on growth, yield and quality of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under inceptisol. International Journal of Research in Agronomy. 7(12): 714-720.
Mahachandramuki, E., Thirukumaran, K., Karthikeyan, R., Sivakumar, R. Sellamuthu, K.M and Prabu kumar, 2023. Influence of super nano urea and nano DAP on growth parameters of rice fallow cotton under high density planting system. International Journal of Plant and Soil Science. 35(19): 711-716.
Mallikarjuna, P.R. 2021. Effect of nano nitrogen and nano zinc nutrition on nutrient uptake, growth and yield of irrigated maize during summer in the Southern Transition Zone of Karnataka. M.Sc. (Ag.) Thesis. University of Agricultural Sciences, Shivmogga, Karnataka, India.
Noubissié, T.J.B., Njintang, N.Y and Dolinassou, S. 2012. Heritability studies of protein and oil contents in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes. International Journal of Innovations in Bio- sciences. 2(3): 162-171.
Panse, V.G and Sukhatme, P.V. 1985. Statistical methods for Agricultural workers. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi. 187-202.
Rajput, J.S., Thakur, A.K., Nag, N.K., Chandrakar, T and Singh, D.P. 2022. Effect of nano fertilizer in relation to growth, yield and economics of little millet (Panicum sumatrense) under rainfed conditions. The Pharma Innovation Journal. 11(7): 153-156.
Sagar, D.R.M.S.V., Dawson, J and Reddy, R.U.K. 2020. Effect of phosphorus and gypsum on growth, yield and economics of groundnut (Arachis hypogea L.). International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences. 9(10): 1635-1638.
- Effect of Sowing Window on Nodulation, Yield and Post – Harvest Soil Nutrient Status Under Varied Crop Geometries in Short Duration Pigeonpea (Cajanus Cajan L.)
- Nanotechnology and Its Role in Seed Technology
- Challenges Faced by Agri Startups in Andhra Pradesh
- Constraints of Chcs as Perceived by Farmers in Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh
- Growth, Yield Attributes and Yield of Fingermillet (Eleusine Coracana L. Gaertn.) as Influenced by Different Levels of Fertilizers and Liquid Biofertilizers
- Consumers’ Buying Behaviour Towards Organic Foods in Retail Outlets of Ananthapuramu City, Andhra Pradesh

