Challenges Faced by Agri Startups in Andhra Pradesh
0 Views
BUNGA HEMALIKITHA*, KADIRI MOHAN, Y. PRABHAVATHI AND B. RAMANA MURTHY
Institute of Agribusiness Management, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati-517 502.
ABSTRACT
Agristartups were recognized as key agents of transformation in India’s agricultural sector, where supportive ecosystems had been fostered to promote innovation and entrepreneurship. However, despite their potential to revolutionize agri-business models and value chains, these startups were found to face challenges that hindered their growth and sustainability. The present article was aimed at identifying and analyzing the challenges encountered by agristartup founders across five key dimensions: financial, technological, operational, marketing, and personal. The findings were based on the study conducted with 40 agristartups followed an exploratory-cum-descriptive research design operating across various districts of Andhra Pradesh. It was revealed that high taxation, limited financial access, lack of scalable technologies, poor infrastructure, disrupted supply chains, and limited mentoring were among the most pressing issues. It was concluded that targeted policy interventions, improved support mechanisms, and ecosystem strengthening were crucial for addressing these multifaceted challenges and for fostering the long-term success of agristartups.
KEYWORDS: Entrepreneurship, Innovation, Policy interventions, Startups, Sustainability.
INTRODUCTION
The agriculture sector, which had been traditionally dependent on conventional methods and practices had undergone a significant transformation driven by innovation, technology, and entrepreneurial enthusiasm considered outcomes of ongoing transitions (Ganga and Roshni, 2022). At the forefront of this transformation, agristartups were identified as key catalysts for technological change. Unlike traditional enterprises, startups were characterized by their innovative approaches, high risk environments, and potential for rapid growth (Ekhande and Suradkar,2023). The limited success was taken to underscore the importance of understanding both the innovative practices employed and the challenges encountered (Dykha et al., 2022).
Despite their growing impact, agristartups face multiple hurdles including fragmented landholdings, low technology adoption among smallholders, high upfront costs, uncertain returns on investment, and complex legal and policy frameworks. Upon examination, it was revealed that the majority of challenges faced by agristartups were structural, operational, and market- related rather than technological (Kumar et al., 2024 and Pandey et al., 2024). Therefore, this study was aimed to assess the core challenges faced by agristartups in Andhra Pradesh and offer practical insights for ecosystem enhancement.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The study followed an exploratory-cum- descriptive research design to Identify and analyze the challenges faced by agristartups in Andhra Pradesh. A total of 40 startups were purposively selected, and data was collected through a semi-structured interview schedule. The identified challenges were categorized into five areas: financial, technological, operational, marketing, and personal. The responses of the agristartups were collected through interview method and were analyzed using Garett ranking Technique.
Garett ranking technique helped to identify and prioritize the most significant challenges faced by respondents based on individual rankings. Each respondent was asked to rank challenges, with the most significant challenge given the highest priority as Rank I. This ranking method helped in identifying and analyzing the major challenges systematically and these ranks were converted into scores using a specific formula to calculate present position. The converted scores were then averaged to determine the Garett mean score for each challenge. The challenge with the highest mean score was considered the most critical. This technique provides a systemic and quantitative way to analyze subjective opinions.
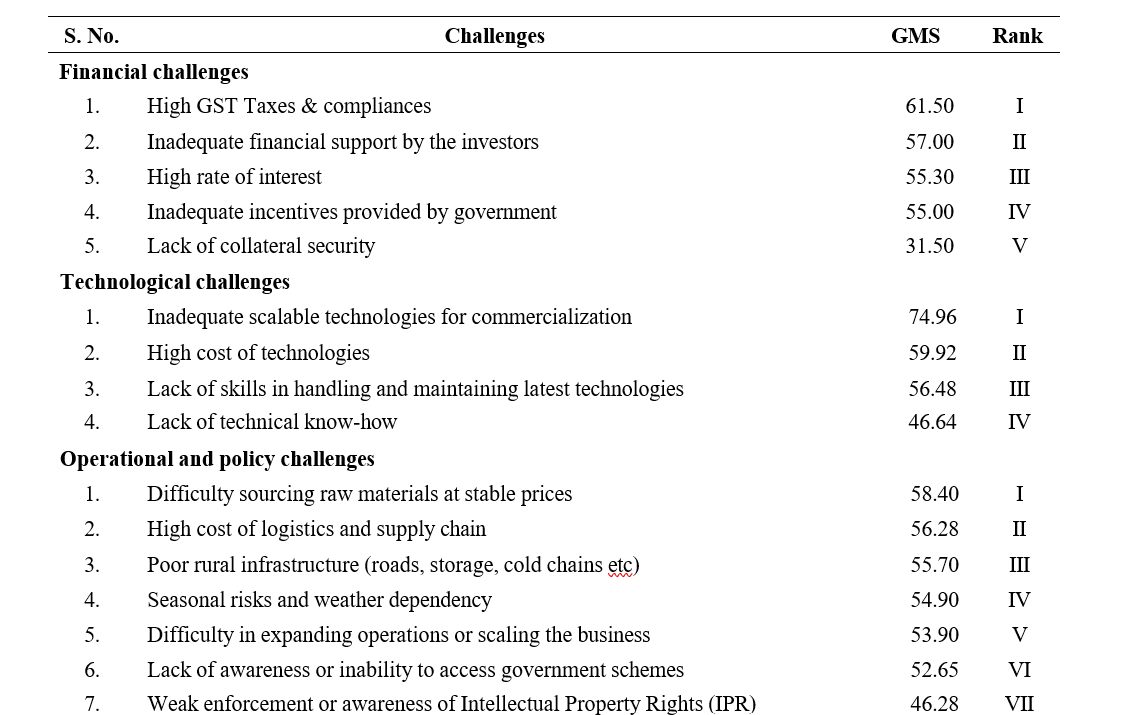
Table 1. Challenges faced by Agristartups (n=40)
The tool used for challenges analysis in this study was Garett Ranking Technique. The method involves calculating the percentage position for each rank using the formula:
Percent position = 100 * (Rij – 0.5)/Nj Where,
Rij = rank given for ith constraint by jth individual
Nj = number of constraint ranked by jth individual
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The challenges were studied under five sub-headings which included financial, technological, operational and policy, marketing and personal challenges faced by the AgriStartup founders. The major challenges were identified and prioritized as follows;
Results from the Table 1 interfered that in financial challenges that High Goods and Service taxes and compliances emerged as the most critical issue (Rank I) with Garett mean score (61.50), Inadequate financial support by investors (Rank II), High rate of interest (Rank III), inadequate incentives provided by the government (Rank IV), and the Lack of collateral security was considered the least severe in this category (Rank V).
In technological challenges, the most significant barrier was Inadequate scalable technologies for commercialization (Rank I) with Garett mean score (74.96). This was followed by the high cost of technologies (Rank II), lack of skills in handling and maintaining latest technologies (Rank III), and lack of technical know-how (Rank IV).
Among operational and policy challenges it is revealed that, difficulty in sourcing raw materials at stable prices was ranked highest (Rank I) with Garett mean score (58.40), followed by high cost of logistics and supply chain (Rank II) poor rural infrastructure (roads, storage, cold chains etc) (Rank III). seasonal risks and weather dependency (Rank IV), difficulty in expanding operations or scaling the business was ranked fifth (Rank V). lack of awareness or inability to access government schemes came sixth (Rank VI), and the lowest-ranked issue was Weak enforcement or awareness of Intellectual Property Rights (Rank VII).
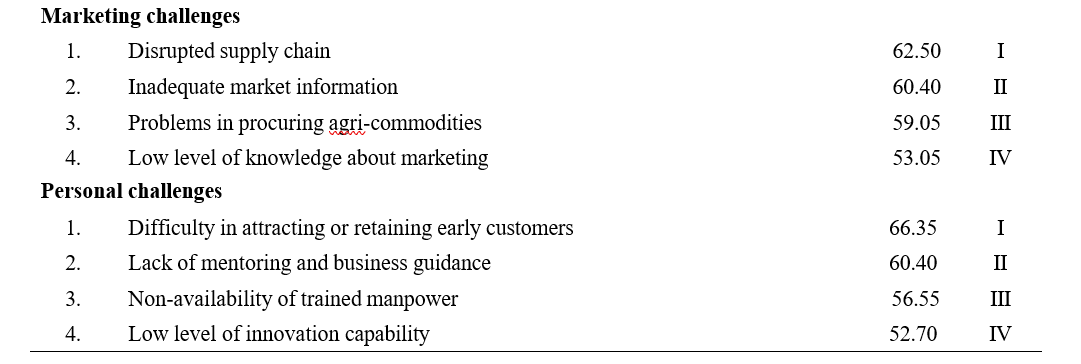
With regards to marketing challenges, the descending orders of the ranked challenges include: disrupted supply chain was the most pressing concern (Rank I) with Garett mean score (62.40), inadequate market information (Rank II), problems in procuring agri-commodities (Rank III), and low level of knowledge about marketing (Rank IV).
Regarding the personal challenges, difficulty in attracting or retaining early customers was ranked first (Rank I) with Garett mean score (66.35), followed by lack of mentoring and business guidance (Rank II), non- availability of trained manpower (Rank III), and low level of innovation capability (Rank IV).
The findings indicated that agristartups were constrained by financial hurdles, with high Goods and Service taxes, limited investor support, and lack of government incentives affecting their growth. Technological adoption was hindered by the absence of scalable solutions, high costs, and insufficient technical skills. Operationalefficiency was impactedby raw material instability, high logistics costs, poor infrastructure, and limited access to government support. Marketing challenges were disrupted supply chains and inadequate market knowledge, while personal challenges included customer acquisition difficulties, lack of mentoring, and limited innovation. These challenges reflected systemic gaps requiring targeted policy, financial, and capacity- building interventions.
The study concluded that issues such as limited access to finance, inadequate infrastructure, lack of scalable technologies, high taxation, disrupted supply chains, and insufficient mentorship had significantly hindered their growth and sustainability. It was further emphasized that without targeted policy interventions, enhanced support systems, and a strengthened entrepreneurial ecosystem, the long-term viability of these startups could not be ensured.
LITERATURE CITED
Dykha, M., Mohylova, A., Ustik, T., Bliumska-Danko, K., Morokhova, V., & Tchon, L. (2022). Marketing of start-ups and innovations in agricultural entrepreneurship. Journal of Agriculture and Crops, 8(1), 27-34.
Ekhande, Y.S. and Suradkar, D.D. (2023). Regression Analysis of Entrepreneurial Behaviour of Sweet Orange Growers. Gujarath Journal of Extension Education 35(1):1-3.
Ganga, D. and Roshni, B. (2022). Socio-Economic Profile of cultivator Cultivated Gar-13 Variety of Rice. Gujarath Journal of Extension Education 33(1):30-32.
Kumar, K., Babu, T. R., & Deshmukh, S. S. (2024). Nurturing Growth: Agri-Startup Landscape in India and the Challenges Ahead. Research on World Agricultural Economy, 5(2), 131-149.
Pandey, A., Sharma, V. K., & Gautam, V. N. (2024). A review: The emerging challenges and opportunities for Agri-startup in India. International Journal of Agriculture Extension and Social Development, 7, 148–150.
- Effect of Sowing Window on Nodulation, Yield and Post – Harvest Soil Nutrient Status Under Varied Crop Geometries in Short Duration Pigeonpea (Cajanus Cajan L.)
- Nanotechnology and Its Role in Seed Technology
- Challenges Faced by Agri Startups in Andhra Pradesh
- Constraints of Chcs as Perceived by Farmers in Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh
- Growth, Yield Attributes and Yield of Fingermillet (Eleusine Coracana L. Gaertn.) as Influenced by Different Levels of Fertilizers and Liquid Biofertilizers
- Consumers’ Buying Behaviour Towards Organic Foods in Retail Outlets of Ananthapuramu City, Andhra Pradesh

